Where is the Power Converter in my RV?
DISCLAIMER: AS AN AMAZON ASSOCIATE I EARN FROM QUALIFYING PURCHASES. THIS POST CONTAINS AFFILIATE LINKS THAT WILL REWARD ME MONETARILY OR OTHERWISE WHEN YOU USE THEM TO MAKE QUALIFYING PURCHASES. FOR MORE INFORMATION, PLEASE READ MY EARNINGS DISCLAIMER.
|
The power converter is usually installed in or as a part of the breaker box (or the load center). If your RV electric system has both the circuit breakers of 120 volts and fuses of 12 volts direct current on a single panel, then it has the power converter as part of that single panel.
When your vehicle is in a parking mode and connected to utility shoreline AC power, your incoming current of 110 volts will be powering all your Alternating Current (AC) devices and 12 volt DC (Direct Current) devices through a converter (as well as RV batteries in order to keep them fully charged). It is different from the inverter, which does exactly the opposite.
Within the RV power system, they are both necessary and serve different needs:
- Converter. This device is in charge of turning standard 110VAC (Alternating Current) utility power into 12VDC (Direct Current). It means it will change your AC current into DC, as well as take it a step down from 110 volts to 12 volts.
- Inverter. This device will bring 12 volts up to 110/120-volt current and change DC power (that is usually supplied by your batteries or solar system) into AC power that most appliances use.
The complete RV power setup will include both inverter and converter systems that sometimes could actually come as one device and take a lot less space. They are called “inverter-chargers”.
The converter in an RV is usually installed in the DC distribution panel or NEXT to the DC distribution panel (or outside the panel). Very often converter is simply placed BESIDES THE BATTERIES (which does make sense, considering that it is supposed to charge them).
In this video, you can see very clearly where power converters are commonly installed. Other information is useful too:
Making sure your converter is in a working condition any time you notice your power system “acting up” (weak lights, etc), is a good practice. As a side note, higher quality converters are more likely to produce a better charge job than cheaper versions.
Where to find a converter in RV?
There are usually two types of electrical systems employed in a recreational vehicle. They are completely independent and work side-by-side:
- 110VAC-120VAC (Alternating Current). This system is used to power your AC devices and appliances that demand a lot of energy. For example air conditioning, TV, microwave, etc.
- 12VDC (Direct Current). This type of system uses batteries or a converter for supplying power to your electronic devices via DC current. Quite a few things are powered by 12 volts DC in your camper and that includes lights, furnaces, fans, and some refrigerators.
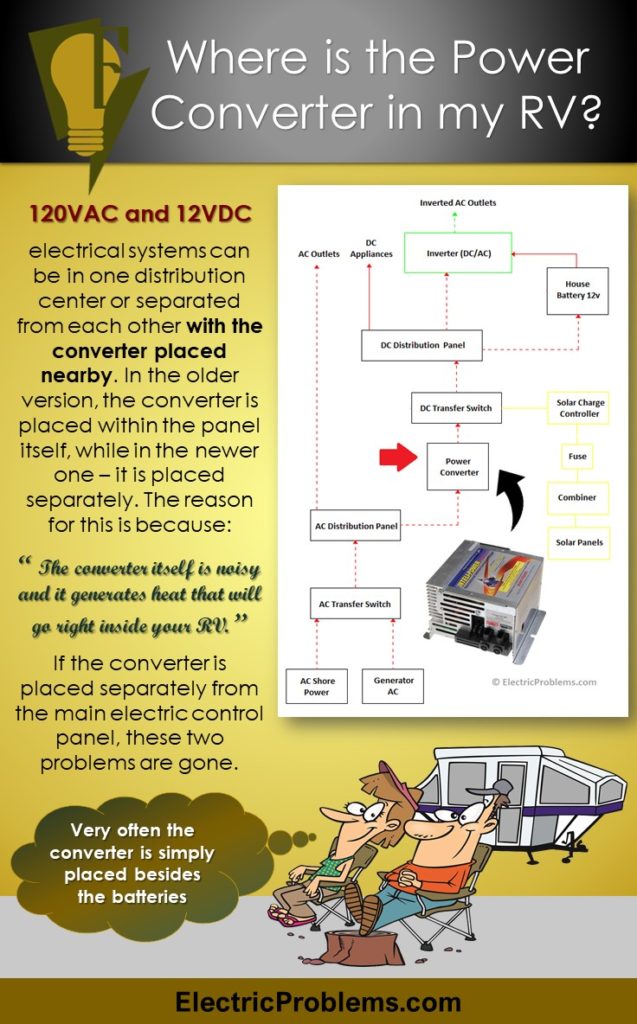
These systems can be in one distribution center or separated from each other with the converter placed nearby. Converters have two major functions and if the converter is not working you will have two problems:
- 12VDC. You will have no 12VDC power for your equipment.
- Batteries. Your batteries will not be charged! A bummer!
This is a typical diagram for wiring a converter and its location within the RV electrical system:
Converter setups could be different and here is another example:
Below is a nice video that will give you an overview of the RV electrical distribution center. The older and the newer version are being compared.
One main difference between the two panels is actually where the converter is placed. In the older version, the converter is placed within the panel itself, while in the newer one – it is placed separately.
The reason for this is because the converter itself is noisy and it generates heat that will go right inside your RV (the older version). When placed separately from the main electric control panel, these two problems are gone (the newer version).
Here is more information (feel free to save this infographic for future reference) .
Need to replace your old converter-charger?
Here are some popular converter options for you:
These inverter chargers could work really well for you if you are limited on space and need an inverter as well. This is a sine-wave version (more expensive, but worth it):
And this is a modified sine wave version (could do just fine on not so sensitive equipment, in case are on the budget):

Click on the white button above to find your electrician!